The life expectancy of a mosquito is typically around two weeks. Mosquitoes, those tiny bothersome insects that are known for their irritating bites, have a relatively short lifespan.
With an average life expectancy of about two weeks, these insects go through a complete life cycle consisting of four stages: egg, larva, pupa, and adult.
While some species may live longer, the majority of mosquitoes only live for a short period of time.
However, during their brief existence, they can cause significant annoyance and even transmit diseases such as malaria, dengue fever, and Zika virus.
Understanding the lifespan of mosquitoes is crucial in developing effective strategies to control their populations and mitigate the risks they pose to human health.
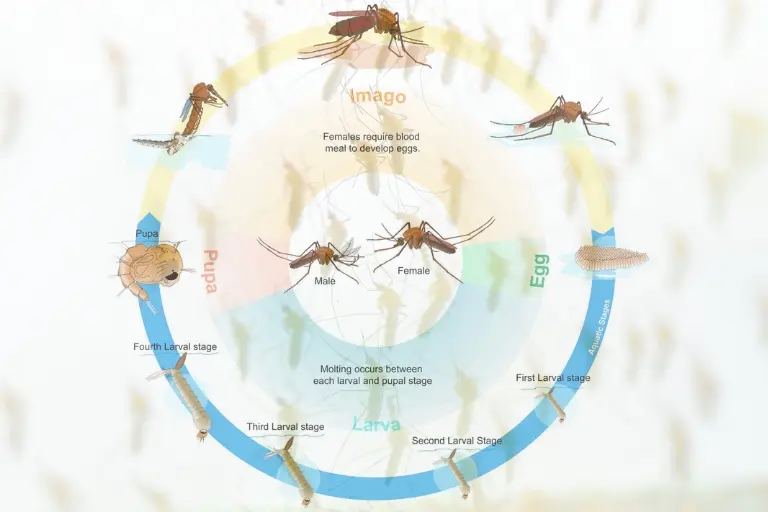
The Life Cycle Of A Mosquito: An Introduction
Understanding the life cycle of a mosquito is crucial when it comes to controlling and preventing its population.
Mosquitoes, those pesky blood-suckers, go through a fascinating four-stage life cycle. These stages involve the transformation from an egg to an adult mosquito capable of spreading diseases.
So, let’s dive into each stage of a mosquito’s life cycle and discover the wonders it holds.
The Four Stages Of A Mosquito’s Life Cycle
Mosquitoes undergo four distinct stages during their life cycle, each one marked by remarkable changes in their appearance and behavior.
These stages are:
- Egg stage
- Larva stage
- Pupa stage
- Adult stage
brief Explanation Of Each Stage
Now, let’s take a closer look at each stage of a mosquito’s life cycle:
Egg Stage
The life cycle of a mosquito begins with the female laying her eggs, usually near or on standing water.
These eggs can be found individually or clustered together and float on the water’s surface.
Each female mosquito can lay hundreds of eggs at a time, depending on the species.
Larva Stage
After the eggs hatch, tiny mosquito larvae emerge. At this stage, the larvae live in the water and have elongated bodies, often resembling small worms.
They breathe through a siphon tube that reaches the surface, allowing them to obtain oxygen.
Mosquito larvae feed on organic matter and microorganisms present in the water.
Pupa Stage
Once the larvae have grown and molted, they enter the pupa stage. The pupa, also known as a “tumbler,” is characterized by a comma-shaped body.
Unlike the larvae, pupae do not feed. Instead, they undergo a transformation inside a protective case called a pupa case.
This stage is crucial for the mosquito’s development and preparation for adulthood.
Adult Stage
After spending a few days as pupae, a fully developed adult mosquito emerges from the pupa case.
The adult mosquito rests on the water’s surface before taking its first flight into the air.
At this stage, female mosquitoes seek blood meals to provide essential nutrients for egg production. Males, on the other hand, feed on nectar or plant juices.
How Long It Takes For A Mosquito To Complete Its Life Cycle
The duration of a mosquito’s life cycle can vary depending on several factors such as temperature, species, and environmental conditions.
In optimal conditions, the life cycle from egg to adult usually takes around 10 to 14 days.
However, some species can complete their life cycle within as little as four days or as long as a month.
The Short But Busy Life Of A Mosquito
The mosquito’s life expectancy may be surprisingly short, ranging from a few weeks to a couple of months.
In this fast-paced life, these tiny insects make the most of their time by buzzing around, searching for a blood meal and reproducing at a rapid rate.
Have you ever wondered about the life expectancy of a mosquito?
These tiny creatures that often find their way into our homes and gardens actually lead to a short but busy existence.
Understanding the life cycle and average lifespan of a mosquito is crucial when it comes to controlling these pests effectively.
We will explore the factors that can affect a mosquito’s lifespan and discuss the importance of studying mosquito life expectancy for pest control measures.
Average Lifespan Of A Mosquito
The average lifespan of a mosquito varies depending on various factors. However, in general, a mosquito’s life cycle can be broken down into four stages: egg, larva, pupa, and adult.
From the moment a mosquito egg hatches into a larva, it goes through a series of molts and transformations before reaching adulthood.
This entire process takes about 8 to 10 days for some species, while others may take up to a month.
Once a mosquito reaches adulthood, its lifespan can range anywhere from a few days to a couple of months.
Female mosquitoes, known for their blood-sucking behavior, typically live longer than males due to their additional energy demands for reproducing.
On average, a female mosquito can live for about 2 to 4 weeks, while males generally have a shorter lifespan of about one to two weeks.
Factors That Can Affect A Mosquito’s Lifespan
Several factors can influence a mosquito’s lifespan.
Some of these factors include:
- Environmental conditions: Mosquitoes thrive in warm and humid environments, so the availability of water and temperature can significantly impact their lifespan. In favorable conditions, mosquitoes can live longer and reproduce at a faster rate.
- Species: Different species of mosquitoes have varying average lifespans. For instance, the Aedes aegypti mosquito, which is known to transmit diseases like dengue and Zika, has a relatively short lifespan of about two to four weeks.
- Feeding habits: Female mosquitoes require blood meals for egg production, which can affect their lifespan. The ability to find suitable hosts for blood feeding plays a crucial role in their survival and overall lifespan.
- Predators and control measures: Mosquitoes face various natural predators, such as birds, bats, and dragonflies, which can affect their population density and lifespan. Additionally, the use of mosquito control methods, like insecticides and mosquito repellents, can also impact their survival rates.
Importance Of Understanding Mosquito Life Expectancy For Pest Control
Studying and understanding the life expectancy of mosquitoes is vital for effective pest control strategies.
By gaining insights into their lifespan, scientists and pest control experts can develop targeted approaches to manage and reduce mosquito populations.
This knowledge allows them to focus on interrupting breeding cycles or implementing control measures during the mosquito’s most vulnerable stages, such as targeting larvae in standing water or using insecticides when adult mosquitoes are most active.
Moreover, understanding mosquito life expectancy is crucial for the prevention and control of mosquito-borne diseases.
By studying the lifespan of disease-carrying mosquitoes, researchers can assess the risk of disease transmission and develop appropriate prevention and control measures.
This information plays a crucial role in public health initiatives and helps in protecting communities from the harmful effects of mosquito-borne illnesses.
The Surprising Lifespan Of Female Mosquitoes
Female mosquitoes have a surprisingly longer lifespan compared to their male counterparts.
We will delve into the reasons behind this disparity and explore how female mosquitoes reproduce, as well as the impact it has on their lifespan.
We will also discuss the crucial role of blood meals in determining the longevity of female mosquitoes.
Why Female Mosquitoes Live Longer Than Males
There are several factors that contribute to the extended lifespan of female mosquitoes. One of the primary reasons is the difference in their biology.
Male mosquitoes do not feed on blood like females do. Instead, they primarily rely on plant nectar for their sustenance. This difference in diet plays a significant role in their lifespan.
Moreover, female mosquitoes have evolved certain physiological adaptations that enhance their longevity.
For instance, they have a larger body size than males, which allows them to store more energy reserves for survival.
Additionally, female mosquitoes have a more efficient immune system, providing better protection against diseases and extending their lifespan.
How Female Mosquitoes Reproduce And Impact On Their Lifespan
The reproductive process of female mosquitoes influences their lifespan. After mating, female mosquitoes require a blood meal to nourish their eggs.
This blood meal provides them with the necessary nutrients to produce and develop their offspring.
However, it also exposes them to potential risks, such as encountering predators or becoming infected with diseases.
The act of reproducing and laying eggs requires a significant amount of energy, which further affects their overall lifespan.Once the eggs are laid, female mosquitoes experience a decline in their physiological functions, resulting in a shorter remaining lifespan.
The Role Of Blood Meals In Female Mosquito Lifespan
Female mosquitoes rely on blood meals for both reproduction and survival. The frequency and availability of blood meals directly impact their lifespan.
When blood is scarce, mosquitoes may enter a state of dormancy or suspend their reproductive activities to conserve energy.
Conversely, a readily available source of blood increases their chances of successfully laying eggs and ensures a more prolonged lifespan.
Environmental Factors Influencing Mosquito Lifespan
Environmental factors play a crucial role in influencing the lifespan of mosquitoes.
Temperature, humidity, availability of water sources, and access to suitable breeding grounds all impact the life expectancy of these disease-carrying insects.
Understanding these factors can help in implementing effective mosquito control strategies.
Environmental factors play a significant role in determining the lifespan of mosquitoes. Temperature, humidity, and other factors can greatly influence how long these pesky insects live. In this section, we will delve into the impact of temperature, humidity, and other environmental factors on mosquito lifespan.
The Impact Of Temperature On Mosquito Life Expectancy
Temperature is a critical factor affecting the life expectancy of mosquitoes. These tiny creatures are cold-blooded and rely on environmental temperatures to regulate their bodily functions.
The duration of a mosquito’s lifespan is directly proportional to the ambient temperature it is exposed to.
Hot temperatures can drastically reduce the lifespan of mosquitoes. High heat can accelerate metabolic processes within their bodies, causing them to age more rapidly.
Excessive temperature can also disrupt their developmental cycles, preventing them from reaching their full potential lifespan.
On the other hand, lower temperatures can extend the life expectancy of mosquitoes.
A study conducted by scientists found that temperatures between 75 to 85 degrees Fahrenheit are optimal for the survival and reproduction of most mosquito species.
Under these conditions, mosquitoes can live for a longer duration, allowing them to complete their life cycle and contribute to the perpetuation of their species.
However, extreme heat waves or cold snaps can significantly reduce their overall lifespan.
How Humidity Affects The Lifespan Of Mosquitoes
Humidity is another crucial environmental factor that influences mosquito lifespan.
These bloodsuckers thrive in areas with high moisture content, as it provides necessary breeding conditions. However, the level of humidity can impact their overall longevity.
High humidity levels can shorten the lifespan of mosquitoes. Excessive moisture in the environment can lead to the growth of harmful fungi and bacteria, which can infect and kill these insects.
Moreover, high humidity can accelerate water evaporation from their bodies, leading to dehydration and ultimately causing their demise.
Conversely, low humidity levels can prolong their lifespan. In drier conditions, mosquitoes are less susceptible to fungal and bacterial infections.
They also retain more moisture within their bodies, reducing the risk of dehydration.
Therefore, areas with lower humidity can facilitate longer lifespans for mosquitos, allowing them to continue their pesky existence.
Other Environmental Factors That Can Influence Mosquito Lifespan
Apart from temperature and humidity, several other environmental factors can impact the lifespan of mosquitoes.
These include:
- Availability of breeding sites: Mosquitoes require stagnant water for breeding purposes. The accessibility of suitable breeding grounds can determine their population density and, consequently, their lifespan.
- Presence of predators: Mosquitoes have numerous natural predators, including dragonflies, birds, and fish. Areas with a higher presence of predators can significantly reduce mosquito lifespan as they become prey.
- Exposure to insecticides: Mosquitoes are vulnerable to chemical interventions such as insecticides. The use of insecticides in an area can actively impact their lifespan, particularly if the pesticides are effective in reducing their population.
- Climate change: The ongoing changes in our climate can have significant implications for mosquito lifespan. Alterations in temperature patterns, precipitation levels, and overall weather conditions can directly affect their development, reproduction, and longevity.
Understanding the environmental factors that influence mosquito lifespan is crucial in developing effective strategies for mosquito control.
By manipulating these factors, we can potentially reduce their lifespans, limit their population growth, and minimize the risks they pose to human health.
The Lifespan Of Mosquitoes: Myth Vs. Reality
Contrary to popular belief, the lifespan of a mosquito is not as long as many think.
While myth has it at weeks or even months, the reality is that the life expectancy of a mosquito is often much shorter, typically ranging from a few days to a couple of weeks.
Mosquitoes are notorious pests that can disrupt our outdoor activities, spread diseases, and leave us itching for days.
With their constant buzzing and relentless bites, it’s natural for us to wonder how long these pesky insects live.
We’re going to explore the lifespan of mosquitoes and debunk some common misconceptions.
By dispelling myths and providing accurate information, we can gain a better understanding of these tiny creatures and take the necessary steps to control and prevent their presence.
Common misconceptions about mosquito lifespan
There are several common misconceptions surrounding the lifespan of mosquitoes.
Let’s take a closer look at these myths:
- Myth: Mosquitoes live for only a few days or weeks.
- Myth: All mosquitoes have the same lifespan.
- Myth: All mosquito species live equally long.
Dispelling myths and providing accurate information
In reality, the lifespan of mosquitoes varies depending on various factors, including the species, environmental conditions, and availability of food sources.
While some mosquito species may indeed only live for a few days or weeks, others can live for several months.
For instance, the Aedes mosquito, known for transmitting diseases such as dengue and Zika, typically lives between two to four weeks.
On the other hand, the Anopheles mosquito, responsible for spreading malaria, can live anywhere from two weeks to a month.
To gain a better understanding of mosquito lifespan, it’s essential to recognize that male and female mosquitoes have different life expectancies.
Male mosquitoes generally have a shorter lifespan of about one to two weeks, whereas female mosquitoes can live significantly longer.
The reason behind this difference lies in their reproductive roles – female mosquitoes require a longer lifespan to lay multiple batches of eggs throughout their lives.
The importance of accurate knowledge for mosquito control and prevention
Accurate knowledge about mosquito lifespan is crucial for effective mosquito control and prevention.
By understanding their life cycle and lifespan, we can implement targeted strategies to reduce mosquito populations and minimize the risk of diseases they carry.
For instance, knowing that certain species live longer allows organizations and individuals to focus their efforts on controlling those specific species.
This knowledge empowers us to make informed decisions when it comes to using preventive measures such as insecticides, elimination of breeding sites, and the use of barriers like screens or nets.
FAQs On What Is The Life Expectancy Of A Mosquito
How Long Can A Mosquito Live In A House?
A mosquito can live for about two weeks in a house.
What Is The Lifespan Of A Mosquito Without Blood?
A mosquito can survive for a few days without blood but needs it to lay eggs and reproduce. The lifespan of a female mosquito varies depending on the species and environmental factors. Generally, it can live for about 2 to 3 weeks.
What Kills Mosquitoes?
Mosquitoes can be killed using mosquito repellents, and insecticides, or by eliminating their breeding grounds. These methods help to control and prevent mosquito populations, reducing the risk of mosquito-borne diseases
Where Do Mosquitoes Go In The Winter?
Mosquitoes disappear in winter, as colder temperatures slow down their activity. They lay eggs or enter a hibernation-like state in water sources, such as ponds and puddles. Some mosquitoes survive by finding shelter in basements or other warm areas.
Final Words
The life expectancy of a mosquito varies depending on several factors such as species, environment, and climate.
While some mosquitoes can live for only a few weeks, others can survive for a few months or even a year.
Understanding the lifespan of mosquitoes is crucial for effective mosquito control strategies and preventing the spread of diseases they carry.
By implementing targeted prevention methods, we can reduce the population of these pesky insects and minimize their impact on our lives.
Stay informed and take necessary precautions to safeguard yourself and your community from mosquito-borne diseases.
