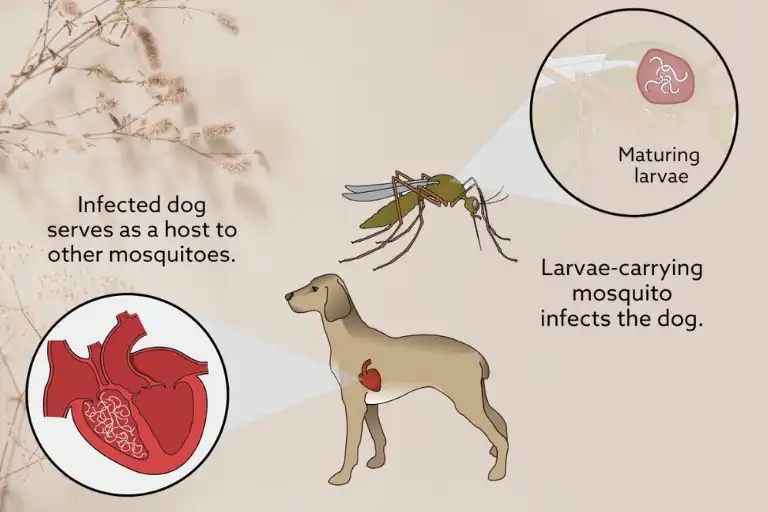
Mosquitoes contract heartworms by feeding on infected animals and spreading the larvae. Heartworms can then mature and reproduce in the mosquito, which can transmit them to other animals through subsequent bites.
The Life Cycle Of The Heartworm Parasite
In order to understand how mosquitoes transmit heartworms, it is essential to explore the different stages of the heartworm life cycle.
These tiny parasites go through several transformations before they reach the stage where they can infect a new host.
Exploring The Different Stages Of The Heartworm Life Cycle
The life cycle of a heartworm begins when an infected adult female heartworm releases her offspring, called microfilariae, into the bloodstream of the host animal.
These microfilariae circulate in the bloodstream for several weeks, maturing into infective larvae.
| Stage | Description |
|---|---|
| Microfilariae | Offspring released by adult female heartworms in the host’s bloodstream. |
| Infective Larvae | Developed microfilariae mature into infective larvae, which are capable of infecting a new host. |
| Mosquito Stage | Mosquitoes become infected with heartworm larvae when they feed on the blood of an infected animal. |
| Heartworm Larvae | Within the mosquito, larvae further mature into their infective stage. |
| Infective Mosquito | The mosquito is now considered an infective mosquito, capable of transmitting heartworms to a new host. |
Understanding The Role Of Mosquitoes In Transmitting Heartworms
Mosquitoes play a crucial role in the transmission of heartworms. When an infected mosquito bites a healthy animal, it injects the larvae into the bloodstream.
These larvae then migrate through the tissues and eventually reach the heart and lungs, where they mature into adult heartworms.
It is important to note that heartworms cannot be transmitted directly from one infected animal to another.
The intermediary role of the mosquito is vital in the transmission process.
Examining The Factors That Contribute To Heartworm Transmission
Several factors contribute to the transmission of heartworms. Firstly, the presence of infected animals in an area increases the likelihood of mosquitoes becoming infected with heartworm larvae.
Infected animals act as reservoirs for the parasite, ensuring a continuous source of heartworm larvae for mosquitoes to pick up.
Additionally, factors such as climate and mosquito populations can influence the transmission of heartworms.
Mosquitoes thrive in warm and humid environments, making these regions more prone to heartworm transmission.
Areas with a high density of mosquitoes provide a greater opportunity for transmission to occur.
Understanding the life cycle of heartworms and the role of mosquitoes in their transmission is essential for pet owners to take preventative measures.
By using effective heartworm prevention methods, such as oral medications and topical treatments, pet owners can ensure their furry companions stay safe from this potentially deadly parasite.
The Mosquito’s Role In Heartworm Transmission
Mosquitoes play a crucial role in the transmission of heartworm disease, carrying and transmitting the microscopic larvae from infected animals to healthy ones.
Understanding how mosquitoes acquire and spread heartworm can help prevent its transmission and protect pets.
Uncovering How Mosquitoes Become Carriers Of Heartworm Larvae
Mosquitoes play a crucial role in the transmission of heartworms, acting as carriers for the development and spread of the disease.
Understanding how mosquitoes become carriers of heartworm larvae is vital in grasping the overall life cycle of this menacing parasite.
The process begins when an infected animal, such as a dog or a cat, harbors adult heartworms in its bloodstream.
These adult worms reproduce and release microscopic baby worms, known as microfilariae, into the bloodstream.
When a mosquito feeds on the blood of an infected animal, it inadvertently ingests these microfilariae along with the blood.
While the mosquito itself is not affected by the heartworm infection, it serves as an unwitting vessel for the transmission of the disease.
The microfilariae ingested by the mosquito then undergo several stages of development within its body, ultimately transforming into infective larvae that can be transmitted to other animals upon subsequent blood meals.
Explaining The Process Of Heartworm Larvae Development Within Mosquitoes
Once inside the mosquito, the microfilariae molt and develop into the infective stage of heartworm larvae.
This development occurs for approximately two weeks and takes place primarily within the mosquito’s external mouthparts and thoracic muscles.
These infective larvae migrate to the mosquito’s salivary glands, ready to be injected into a new host during the mosquito’s next feeding event.
When the mosquito bites another animal, such as a dog or a cat, it injects these infective larvae into the animal’s bloodstream, continuing the heartworm life cycle.
Highlighting The Conditions That Make Mosquitoes Effective Heartworm Transmitters
Mosquitoes are highly effective transmitters of heartworm due to specific conditions that favor the survival and maturation of the infective larvae.
Firstly, mosquitoes thrive in warm and humid environments, where the temperature ranges from 57°F (13.8°C) to as high as 86°F (30°C).
This range facilitates optimal development of the heartworm larvae within the mosquito.
Another crucial factor is the presence of still water sources, such as ponds, puddles, or stagnant pools.
These provide ideal breeding grounds for mosquitoes, allowing them to lay their eggs and continue their life cycle.
Additionally, mosquitoes require a blood meal to complete their reproductive cycle, making them more likely to feed on animals infected with heartworms and facilitate the transmission of the disease.
Understanding the mosquito’s role in heartworm transmission helps emphasize the importance of preventing mosquito bites and protecting our furry friends from this potentially fatal disease.
By minimizing exposure to mosquitoes and implementing preventive measures, such as heartworm medication, we can reduce the risk of heartworm infection and ensure the health and well-being of our beloved pets.
Mosquito Feeding Habits And Heartworm Transmission
Mosquitoes transmit heartworm through their feeding habits, specifically by feeding on an infected animal and then infecting a healthy one with their bite.
The transmission occurs when infected larvae enter a new host through the mosquito’s bite, leading to the development of heartworm disease.
Examining How Mosquitoes Locate And Choose Their Hosts
Mosquitoes are notorious for their ability to find and feed on their hosts, which can include humans and animals alike.
But have you ever wondered how they manage to zero in on their targets with such precision?
To understand this, we need to delve into the fascinating world of mosquito sensory perception.
These tiny insects have a highly developed olfactory system that allows them to detect the chemicals emitted by potential hosts such as carbon dioxide, lactic acid, ammonia, and octanol.
Through a combination of variations in these chemical cues, mosquitoes can accurately locate their next meal.
Not only do mosquitoes possess an acute sense of smell, but they also have specialized receptors on their antennae that detect heat and moisture.
These additional sensory abilities play a crucial role in guiding them toward potential hosts.
Exploring The Feeding Habits Of Mosquitoes And The Risk Of Heartworm Transmission
Mosquitoes rely on fluid intake for survival and reproduction, and their feeding habits are remarkably efficient.
They use their slender, needle-like mouthparts known as proboscis to pierce the skin of their chosen host.
Once successfully inserted, they release saliva that contains anticoagulants, ensuring a steady blood flow into their bodies.
Unfortunately, this feeding process can result in a serious health risk for our beloved pets.
Heartworm disease, caused by the parasite Dirofilaria immitis, is transmitted through the bite of an infected mosquito.
When an infected mosquito feeds on an animal, it ingests microfilariae, the immature heartworm stage.
These microfilariae then undergo development within the mosquito, eventually maturing into infective larvae.
When the infected mosquito subsequently feeds on another animal, it injects these infective larvae into the new host’s bloodstream.
These larvae migrate through the host’s tissues, eventually reaching the heart and lungs, where they mature into adult heartworms.
This ongoing cycle perpetuates the transmission of heartworm disease among animals.
Delving Into The Factors That Influence Mosquito Feeding On Heartworm-infected Animals
While mosquitoes feed on various hosts, some factors influence their preference for heartworm-infected animals.
One determinant is the presence of specific chemicals released by already-infected animals, making them more attractive to mosquitoes.
Additionally, the age and size of the mosquito, as well as the blood meal size preference, can influence their feeding behavior.
For instance, older mosquitoes tend to have a greater likelihood of transmitting heartworm disease as they have had more opportunities to acquire the infection.
Factors Affecting Heartworm Transmission Rates
Understanding the factors that contribute to heartworm transmission rates is crucial for effectively preventing this dangerous disease in our furry friends.
Various environmental, climatic, and geographical factors come into play, influencing the activity of mosquitoes and the prevalence of heartworm.
We will delve into these factors to gain a deeper understanding of how they impact heartworm transmission rates.
Discussing Environmental Factors That Influence Mosquito Activity And Heartworm Transmission
For heartworm transmission to occur, mosquitoes need to be present in ample numbers.
The mosquito population is greatly influenced by environmental factors that affect their breeding and survival.
Let’s take a closer look at these environmental factors:
- Temperatures: Mosquitoes are more active in warmer temperatures, with their activity peaking during the summer months. Warmer climates create a conducive environment for mosquito breeding and the spread of heartworms.
- Humidity: High humidity levels provide the necessary moisture for mosquito larvae to survive and develop. Areas with high humidity tend to have a higher mosquito population, increasing the risk of heartworm transmission.
- Standing water: Mosquitoes lay their eggs in standing water, so areas with stagnant water sources like ponds, puddles, and neglected containers serve as ideal breeding grounds. Eliminating standing water helps minimize mosquito breeding and reduces the risk of heartworm transmission.
- Vegetation: Overgrown vegetation provides shelter and hiding places for mosquitoes, making it easier for them to avoid predators and survive. Areas with dense vegetation may have higher mosquito populations, increasing the risk of heartworm transmission.
Examining How Climate And Weather Patterns Impact Heartworm Prevalence
The climate and weather patterns of an area have a significant impact on heartworm transmission rates.
Let’s explore how these factors contribute to the prevalence of heartworm:
- Temperature fluctuations: Drastic temperature changes can affect the survival and growth of mosquitoes and heartworm larvae. Fluctuating temperatures can disrupt the heartworm life cycle and limit transmission.
- Rainfall: Rainfall patterns can influence mosquito breeding opportunities. Heavy rainfall can create more breeding grounds for mosquitoes, resulting in increased heartworm transmission rates.
- Drought: On the other hand, prolonged droughts can reduce the availability of standing water, limiting mosquito breeding sites and thereby reducing heartworm transmission.
Addressing The Role Of Geographic Location And Population Density In Heartworm Transmission
The geographical location and population density of an area play crucial roles in heartworm transmission.
Let’s examine how these factors affect the prevalence of heartworm:
- Geographic location: Heartworm transmission rates vary based on geographic location. Regions with warmer climates and higher mosquito populations tend to have higher rates of heartworm infection. However, it’s important to note that heartworm can still be a threat in cooler regions, especially in urban areas where environmental conditions can support mosquito survival.
- Population density: Areas with a higher population density, particularly near each other and to mosquito breeding grounds, are at a higher risk of heartworm transmission. Increased numbers of infected animals can contribute to the overall heartworm burden in a community.
By understanding and considering these various factors, pet owners and veterinarians can take appropriate measures to protect their furry companions.
Preventive measures like regular heartworm testing, the use of mosquito repellents, and administering heartworm preventives are essential for keeping our pets safe and healthy.
Preventing Mosquito-borne Heartworm Infections
When it comes to protecting our beloved pets from the risks of mosquito-borne heartworm infections, prevention is key.
By understanding the effective preventive measures available and prioritizing regular heartworm testing and veterinary care, pet owners can significantly reduce the chances of their furry companions falling victim to this potentially life-threatening disease.
Highlighting Effective Preventive Measures For Pet Owners And Their Furry Companions
To shield our pets from the dangers of heartworm disease, pet owners must take proactive steps to prevent mosquito bites.
Here are a few effective preventive measures:
- Administering heartworm preventives prescribed by your veterinarian regularly and as directed. These medications target immature heartworm larvae and prevent them from developing into adult worms that can cause severe damage.
- Ensuring your pets are up-to-date with their vaccinations and overall health care. A healthy and strong immune system can better defend against heartworm infections.
- Maintaining a clean and pest-free environment. Regularly remove stagnant water sources such as birdbaths and flower pots to eliminate breeding grounds for mosquitoes.
- Using mosquito repellents specifically formulated for pets. These products help repel mosquitoes and reduce the risk of bites.
- Limiting outdoor activities during peak mosquito hours, which are typically dawn and dusk. Mosquito activity tends to be highest during these periods, increasing the chances of exposure.
Understanding The Importance Of Regular Heartworm Testing And Veterinary Care
Regular heartworm testing and veterinary care play a crucial role in keeping our pets healthy and protected.
Here’s why:
- Heartworm testing allows veterinarians to detect the presence of heartworm larvae in the bloodstream at an early stage, enabling timely treatment if necessary.
- Annual heartworm testing is recommended by veterinarians, even for pets already on preventive medications. This ensures that the medications are working effectively and that any potential concerns are addressed promptly.
- Veterinary care provides an opportunity for comprehensive examinations, including checking for any signs or symptoms of heartworm disease. Early detection can lead to more successful treatment outcomes.
Exploring Alternative Methods Of Mosquito Control To Reduce Heartworm Transmission
In addition to traditional preventive measures, exploring alternative methods of mosquito control can further reduce the transmission of heartworm.
Some of these methods include:
| Method | Advantages |
|---|---|
| Introducing mosquito-eating fish to outdoor water sources | These fish feed on mosquito larvae, reducing the population of potential heartworm carriers. |
| Planting mosquito-repelling plants | Certain plants, such as citronella, lavender, and marigold, emit scents that repel mosquitoes. |
| Installing mosquito traps | Mosquito traps attract and capture mosquitoes, preventing them from biting pets and spreading heartworm. |
By incorporating these alternative methods into your mosquito control strategy, you can provide an added layer of defense against heartworm disease for your furry friends.
FAQs For How Do Mosquitoes Get Heartworm
How Do Mosquitoes Get Heartworm?
Heartworm is transmitted to mosquitoes when they feed on infected dogs, creating a transmission cycle.
Can Humans Get Heartworm From Mosquitoes?
No, humans are not the natural hosts for heartworm, so they cannot contract it from mosquitoes.
How Long Does It Take For Heartworm To Develop In Mosquitoes?
After feeding on an infected animal, it takes about two weeks for heartworm larvae to mature within mosquitoes.
How Does Heartworm Infect Dogs Through Mosquitoes?
When mosquitoes bite infected dogs, they inject immature heartworm larvae into the dog’s bloodstream, leading to infection.
Final Thoughts
Understanding how mosquitoes get heartworm is essential in preventing the spread of this deadly disease.
By eliminating mosquito breeding grounds, using preventive medications for our pets, and reducing their exposure to mosquitoes, we can keep them safe and healthy.
Remember, protecting our pets is our responsibility, and together we can make a significant impact in reducing the prevalence of heartworm disease.
Let’s prioritize their well-being by staying informed and taking proactive measures.
