Mosquito saliva contains anticoagulant proteins and enzymes that prevent blood clotting. It also contains compounds that cause itching and allergic reactions in humans.
Mosquitoes are infamous for their itchy bites and the diseases they can transmit.
But have you ever wondered what exactly is in their saliva that causes such discomfort?
We will explore the contents of mosquito saliva and the role it plays in their feeding habits.
Mosquito saliva contains anticoagulant proteins and enzymes, which prevent blood from clotting while they feed on their host.
This allows them to obtain a sufficient blood meal to nourish and reproduce. Additionally, mosquito saliva contains compounds that cause itching and allergic reactions in humans.
Understanding the components of mosquito saliva can help researchers develop more effective strategies for preventing mosquito-borne diseases and alleviating the symptoms of mosquito bites.
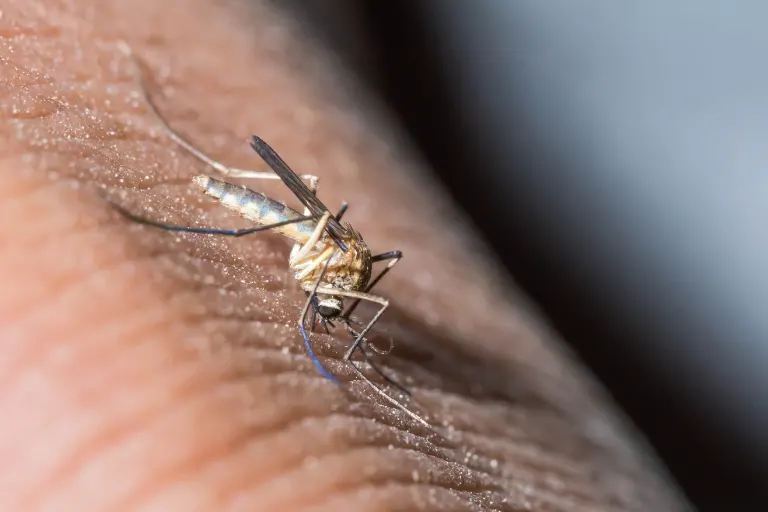
Understanding Mosquito Saliva’s Composition
Mosquitoes are not just pesky insects that cause irritation and itchiness through their bites.
What many people don’t realize is that these tiny creatures inject saliva into our skin when they bite.
The composition of mosquito saliva is a complex mixture of various proteins, enzymes, and bioactive compounds that play a significant role in their feeding process.
Let’s delve deeper into the components that make up mosquito saliva and their effects on the human body.
Proteins And Enzymes Present In Mosquito Saliva
The saliva of mosquitoes contains an array of proteins and enzymes, which serve different purposes during their feeding process.
These components help mosquitoes obtain a blood meal, facilitate the feeding process, and prevent the host’s immune system from detecting and neutralizing them effectively.
- Anopheline Salivary Protein (ASP): ASP is a vital protein found in the saliva of anopheles mosquitoes, responsible for facilitating blood clotting inhibition, allowing them to feed for an extended period. This protein also acts as an anti-inflammatory agent, reducing the host’s immune response to the bite.
- Culex Natriuretic Peptide (CNP): Present in Culex mosquitoes’ saliva, this protein helps regulate blood pressure and fluid balance in the host. It acts as a vasodilator, widening blood vessels to enhance blood flow and facilitate feeding.
- Apyrase: Apyrase is an enzyme found in mosquito saliva that plays a crucial role in blood feeding. Preventing the clotting of blood at the bite site ensures a steady and uninterrupted flow of blood for the mosquito to obtain its meal.
Bioactive Compounds And Their Effects On The Human Body
In addition to proteins and enzymes, mosquito saliva contains various bioactive compounds that influence our body’s response to their bites.
These compounds can elicit different reactions and provoke immune responses, causing the well-known itchiness and swelling.
| Bioactive Compound | Effect on the Human Body |
|---|---|
| Histamine | Causes blood vessels to dilate, facilitating the migration of immune cells to the bite site, resulting in redness and swelling. |
| Serotonin | Acts as a vasodilator and enhances vascular permeability, leading to increased blood flow and localized swelling. |
| Prostaglandins | Trigger inflammation and pain at the bite site as part of the body’s defense mechanism. |
These bioactive compounds, along with the mosquito saliva’s proteins and enzymes, modulate our immune response by altering blood flow, coagulation, and inflammatory reactions.
The combination of these effects contributes to the discomfort experienced after a mosquito bite.
The Role Of Mosquito Saliva In Feeding
Mosquito saliva contains a range of substances that help facilitate feeding.
These include anti-coagulants to prevent blood from clotting, analgesics to numb the bite area, and immune-modulating proteins to suppress the host’s immune response.
How Mosquito Saliva Aids In Blood Feeding
Mosquito saliva plays a crucial role in the blood-feeding of these pesky insects.
It contains a complex cocktail of bioactive molecules that facilitate a successful meal for the mosquito while ensuring minimal disruption to the host.
Let’s dive into the various ways in which mosquito saliva aids in blood feeding.
Inhibiting Host Immune Response For Successful Feeding
In order to successfully feed on blood, mosquitoes need to overcome the host’s powerful immune system.
Mosquito saliva contains a range of proteins and enzymes that help the insect evade and suppress the host’s immune response.
One such protein is believed to inhibit the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines, molecules responsible for triggering an immune response.
Additionally, mosquito saliva contains anti-coagulant compounds that prevent the blood at the feeding site from clotting.
These compounds help maintain blood flow and prevent blood vessels from constricting, ensuring a steady and uninterrupted blood meal for the mosquito.
Inhibiting the host’s immune response and disrupting blood clotting mechanisms are crucial for a mosquito’s successful feeding.
By doing so, mosquitoes can obtain their meal efficiently and minimize the chances of a detected blood source, increasing their chances of survival and reproductive success.
The Itch Factor: How Mosquito Saliva Triggers Irritation
One of the most frustrating aspects of a mosquito bite is the incessant itching that follows.
But have you ever wondered why mosquitoes leave you scratching for days? The answer lies in their saliva.
Allergic Reactions To Mosquito Saliva
Mosquito saliva contains a complex cocktail of proteins and enzymes that can elicit varying reactions in different individuals.
While most people experience mild irritation and itchiness, some individuals may have an allergic reaction to mosquito saliva.
A mosquito bite triggers an immune response in the body, leading to the release of histamines, which are responsible for the initial inflammation and itching.
For individuals who are allergic, this immune response can be exaggerated and result in more severe symptoms.
Histamines And Other Compounds Causing Itchiness
Histamines, the main culprits behind the itching sensation caused by mosquito bites, are vasodilators.
This means they expand the blood vessels around the bite, allowing white blood cells and other immune cells to reach the affected area more rapidly.
In addition to histamines, mosquito saliva contains other compounds that further contribute to the itchiness.
These compounds, such as prostaglandins and proteins, interact with the nerve endings in our skin, triggering the sensation of itchiness.
Mosquito Saliva As A Potential Allergen
While most people only experience temporary discomfort from mosquito bites, some individuals may develop a true allergy to mosquito saliva.
This happens when the immune system mistakenly identifies certain proteins in the saliva as harmful substances.
For those with a mosquito saliva allergy, the immune system responds by releasing an excessive amount of antibodies called immunoglobulin E (IgE).
This antibody triggers a cascade of immune reactions, leading to symptoms such as swelling, hives, and in extreme cases, difficulty breathing.
It’s important to note that developing a true allergy to mosquito saliva is relatively rare, but if you suspect you may be allergic, it’s essential to consult a healthcare professional for proper diagnosis and management.
Potential Health Risks Associated With Mosquito Saliva
Mosquitoes are not only irritating pests but also potential carriers of diseases.
While many people are aware of the diseases transmitted by mosquitoes, what they may not know is that the saliva of these tiny insects plays a crucial role in the transmission process.
Understanding the potential health risks associated with mosquito saliva is essential in order to take the necessary precautions to protect ourselves.
Transmission Of Diseases Through Saliva
When a mosquito bites a human, it injects its saliva into the skin to prevent blood clotting and to help it obtain a meal.
This saliva contains a mix of proteins, enzymes, and other substances that facilitate blood flow and numb the area, making the bite painless.
However, some of the pathogens responsible for diseases such as dengue fever, Zika virus, and malaria can also be present in mosquito saliva.
Specific Pathogens Carried By Mosquitoes
Mosquitoes can carry a wide range of pathogens in their saliva, depending on the region and species.
Here are some of the most common diseases that can be transmitted through mosquito bites:
- Dengue fever
- Zika virus
- West Nile virus
- Malaria
- Chikungunya
These diseases can have serious health implications, ranging from mild symptoms such as fever and rash to severe cases that can lead to long-term complications or even death.
Impact Of Mosquito Saliva On Disease Transmission
The presence of pathogens in mosquito saliva increases the risk of disease transmission. When a mosquito bites a human, it injects saliva into the bloodstream.
This saliva can contain viable pathogens that can directly infect the host.
Additionally, the saliva can also modulate the immune response, making it easier for the pathogens to establish an infection.
The proteins and other components present in mosquito saliva can have immunomodulatory effects, suppressing the immune system’s response and allowing the pathogens to replicate and spread more easily.
This can result in a more severe infection and higher chances of transmission to other individuals.
It is important to note that not all mosquito bites lead to disease transmission, as the presence of pathogens in mosquito populations varies.
However, it is crucial to take precautions and protect against mosquito bites to minimize the risk of exposure to these potentially dangerous diseases.
Mosquitoes are not only irritating pests but also potential carriers of diseases.
While many people are aware of the diseases transmitted by mosquitoes, what they may not know is that the saliva of these tiny insects plays a crucial role in the transmission process.
Understanding the potential health risks associated with mosquito saliva is essential in order to take the necessary precautions to protect ourselves.
Transmission of diseases through saliva
When a mosquito bites a human, it injects its saliva into the skin to prevent blood clotting and to help it obtain a meal.
This saliva contains a mix of proteins, enzymes, and other substances that facilitate blood flow and numb the area, making the bite painless.
However, some of the pathogens responsible for diseases such as dengue fever, Zika virus, and malaria can also be present in mosquito saliva.
Specific pathogens carried by mosquitoes
Mosquitoes can carry a wide range of pathogens in their saliva, depending on the region and species.
Here are some of the most common diseases that can be transmitted through mosquito bites:
- Dengue fever
- Zika virus
- West Nile virus
- Malaria
- Chikungunya
These diseases can have serious health implications, ranging from mild symptoms such as fever and rash to severe cases that can lead to long-term complications or even death.
Impact of mosquito saliva on disease transmission
The presence of pathogens in mosquito saliva increases the risk of disease transmission. When a mosquito bites a human, it injects saliva into the bloodstream.
This saliva can contain viable pathogens that can directly infect the host.
Additionally, the saliva can also modulate the immune response, making it easier for the pathogens to establish an infection.
The proteins and other components present in mosquito saliva can have immunomodulatory effects, suppressing the immune system’s response and allowing the pathogens to replicate and spread more easily.
This can result in a more severe infection and higher chances of transmission to other individuals.
It is important to note that not all mosquito bites lead to disease transmission, as the presence of pathogens in mosquito populations varies.
However, it is crucial to take precautions and protect against mosquito bites to minimize the risk of exposure to these potentially dangerous diseases.
Strategies To Mitigate Allergic Reactions To Mosquito Bites
Mosquitoes are one of the most notorious pests, not only because of the itchy and annoying bites they leave behind but also due to the potential allergic reactions they can trigger.
The saliva of mosquitos is the culprit behind these allergic reactions. Understanding strategies to mitigate these reactions is crucial for those who experience severe discomfort or have allergies to mosquito bites.
We will explore some effective techniques and treatments to help manage allergic reactions and minimize the discomfort caused by mosquito bites.
Mosquito Bite Prevention Techniques
Prevention is always better than cure, and this holds true when it comes to mosquito bites.
By implementing a few preventive measures, you can significantly reduce your chances of being bitten and experiencing allergic reactions.
Consider the following techniques:
- Use mosquito repellents: Apply a mosquito repellent containing DEET or picaridin to exposed skin before heading outdoors.
- Wear protective clothing: Cover your body with long sleeves, pants, and socks to minimize exposed skin.
- Eliminate breeding grounds: Remove standing water in your surroundings, as mosquitos breed in stagnant water. Regularly empty or treat pools, birdbaths, and other potential water sources.
- Install window screens: Ensure the windows and doors of your home have screens to keep mosquitos out.
- Avoid peak mosquito activity: Mosquitos are most active during dawn and dusk, so try to limit your outdoor activities during these times.
Managing Mosquito Bite Symptoms And Itchiness
Mosquito bites can be incredibly itchy and uncomfortable, especially for those who are allergic.
However, there are several measures you can take to alleviate the symptoms and minimize the itchiness:
- Wash the affected area: Wash the mosquito bite with soap and water to remove any potential irritants that may exacerbate the itching.
- Cold compress: Apply a cold compress or ice pack wrapped in a cloth to the mosquito bite for 10-15 minutes to reduce swelling and numb the area.
- Topical treatments: Over-the-counter creams or ointments containing hydrocortisone or calamine can help alleviate the itching and reduce inflammation.
- Oral antihistamines: Taking an oral antihistamine can help relieve the itching and reduce the allergic response. Consult with a healthcare professional for appropriate dosage and recommendations.
Immunotherapy And Desensitization
For individuals who experience severe allergic reactions to mosquito bites, immunotherapy and desensitization may be recommended options to provide long-term relief.
This treatment involves gradually exposing the individual to small, controlled doses of mosquito saliva to build up a tolerance and decrease the body’s allergic response over time.
It is a highly effective approach that can significantly reduce the severity of allergic reactions and alleviate the discomfort caused by mosquito bites.
FAQs Of What Is In Mosquito Saliva
What Substances Are Present In Mosquito Saliva?
Mosquito saliva contains an assortment of proteins, enzymes, anticoagulants, and anesthetics that help the mosquito feed and prevent blood clotting.
How Do Mosquitoes Use Their Saliva?
Mosquitoes inject their saliva into the host’s skin while feeding to keep the blood flowing and prevent it from clotting.
Can Mosquito Saliva Cause An Allergic Reaction?
Yes, some people may experience mild to severe allergic reactions to mosquito saliva, resulting in redness, swelling, itching, and discomfort at the bite site.
Is Mosquito Saliva Dangerous?
While mosquito saliva itself is not dangerous, the bites can transmit diseases such as malaria, dengue, and Zika virus if the mosquito is infected.
Final Words
The components found in mosquito saliva play a vital role in their blood-feeding process.
From anticoagulants to proteins and enzymes, mosquito saliva contains a diverse range of compounds that help them obtain a blood meal.
Understanding the composition of mosquito saliva is crucial in developing effective strategies to control mosquito-borne diseases.
By deciphering this complex mixture, we can further investigate the ways in which mosquito saliva interacts with our immune system and potentially find innovative approaches for prevention and treatment.
Stay informed and take necessary precautions to protect yourself from these bloodsuckers and the diseases they carry.
