A mosquito typically lives for about one to two months after biting someone. Mosquitoes have long been a dreaded pest due to their irritating bites and the potential transmission of diseases.
Understanding the lifespan of these insects is crucial in managing their presence and reducing the risk they pose to human health.
A mosquito’s life cycle consists of four stages – egg, larva, pupa, and adult.
While adult mosquitoes only live for a short period, it is during this time that they are capable of biting humans and spreading diseases such as malaria, dengue fever, and Zika virus.
By gaining insight into the lifespan of mosquitoes, we can better protect ourselves and implement effective control measures to minimize their impact on our lives.
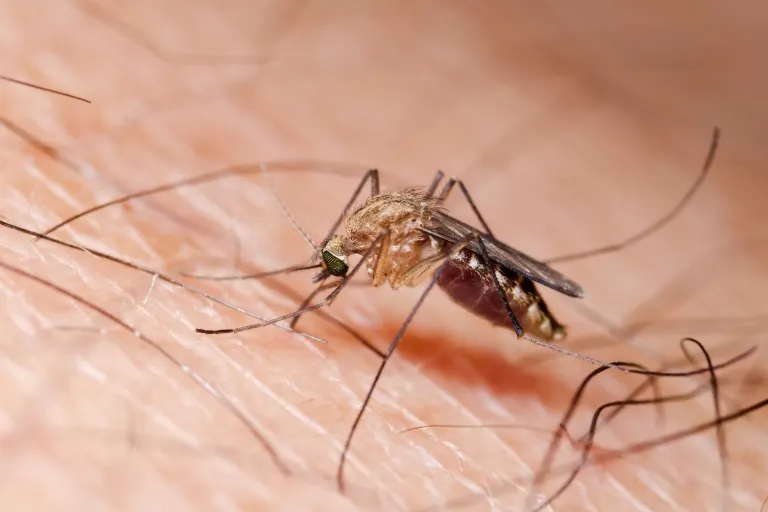
Understanding The Mosquito Life Cycle
Mosquitoes live for about two to three weeks after biting someone. Understanding the mosquito life cycle helps us grasp the duration of their lifespan.
An Introduction To The Mosquito Life Cycle
Understanding the mosquito life cycle is crucial when it comes to combating these pesky creatures and protecting ourselves from their itchy bites.
Mosquitoes undergo a fascinating four-stage development process, which includes egg, larva, pupa, and adult.
Each stage plays a vital role in the overall life cycle, and by gaining insight into this process, we can better comprehend their behavior and take appropriate measures to control their population.
The Four Stages Of Mosquito Development
Mosquitoes progress through four distinct stages of development, each with its unique characteristics and significance.
These stages are as follows:
life cycle begins with the deposition of eggs
The first stage in the mosquito life cycle begins with the deposition of eggs.
Female mosquitoes typically lay their eggs in stagnant water or moist environments, ensuring that they have a suitable environment to hatch.
These tiny, oval-shaped eggs can be found in clusters, carefully attached to surfaces above water or floating in the water itself.
Their number and arrangement vary according to the mosquito species.
From Egg To Larva: Shedding Light On The Initial Phase
Once the eggs are in place, they undergo a process of maturation, leading to the emergence of larvae.
At this stage, the larvae are tiny, almost microscopic, and possess a worm-like appearance.
Despite their minuscule size, these larvae are highly active, constantly wriggling and moving in the water.
Metamorphosis: The Transformation From Larva To Pupa
After consistently growing and feeding in the larval stage, the mosquito undergoes a transformative process called metamorphosis.
This phase marks a significant change in the mosquito’s body structure and behavior.
The larva begins to exhibit peculiar developments, gradually forming distinct body segments, and growing respiratory tubes called siphons.
The pupal stage is often considered a resting phase, as the mosquito does not actively forage for food during this time.
Instead, it remains suspended in the water, with its body encapsulated in a protective casing known as the pupal exoskeleton.
Inside this casing, transformative changes occur, such as the development of wings, legs, and other adult mosquito characteristics.
Emergence: Unveiling The Adult Mosquito
Finally, after the pupal stage, the adult mosquito emerges from its protective casing, ready to take flight.
The emergence takes place as the mosquito splits open the pupal exoskeleton, revealing its delicate wings and long, thin legs.
At this stage, the mosquito has reached its reproductive maturity and is capable of seeking partners, feeding on blood, and continuing the life cycle.
It is important to note that the lifespan of an adult mosquito varies depending on several factors, including the species and environmental conditions.
On average, mosquitoes typically live for several weeks, with some species living up to a few months.
During this time, female mosquitoes actively seek a blood meal for nourishment and to provide essential nutrients for their egg-laying process.
The Lifespan Of An Adult Mosquito
Have you ever wondered how long a mosquito lives after it bites someone?
Understanding the lifespan of these tiny insects can provide valuable insights into their behavior and the transmission of diseases.
Mosquitoes are notorious for their ability to spread diseases such as malaria, dengue fever, and Zika virus, making it crucial to delve into their lifecycles.
Here we’ll explore the factors that affect the lifespan of adult mosquitoes, with a particular focus on the differences between male and female mosquitoes and the role of blood meals in their longevity.
Factors Affecting The Lifespan Of A Mosquito
Several factors come into play when determining the lifespan of a mosquito. These factors include species, environment, and gender.
Generally, the average lifespan of an adult mosquito can range from a few days to several weeks.
Let’s take a closer look at the differences between male and female mosquitoes, which shed light on their distinct lifespans.
Examining The Male Mosquito’s Brief Existence
The male mosquito has a relatively short lifespan compared to its female counterpart.
Usually, male mosquitoes live for only a few days to a week. Interestingly, male mosquitoes do not feed on blood; instead, they nourish themselves with nectar and plant juices, focusing on reproduction as their primary goal.
Once a male mosquito reaches sexual maturity, it seeks out a female to mate.
The Female Mosquito: An Extended Lifespan
Female mosquitoes, on the other hand, have a significantly longer lifespan. Depending on the species, a female mosquito can live anywhere from a few weeks to a couple of months.
This extended lifespan allows female mosquitoes to complete their essential tasks of mating and laying eggs.
Unlike male mosquitoes, female mosquitoes require a blood meal to obtain the necessary nutrients for the development of their eggs.
The Durational Impact Of Mating On The Female Mosquito
Mating plays a crucial role in determining the lifespan of female mosquitoes. After mating, female mosquitoes enter a phase called ‘gravidity,’ during which they rest and develop their eggs.
This period can last for a few days to a week, and the survival rate of a female mosquito decreases during this time.
Once the eggs are matured and ready to be laid, female mosquitoes search for suitable breeding sites, often in stagnant water sources.
Exploring The Role Of Blood Meals In Mosquito Longevity
The main factor that extends the lifespan of female mosquitoes is the availability of blood meals.
When a female mosquito bites a host and feeds on its blood, she obtains the necessary proteins and nutrients to support the growth and development of her eggs.
A single blood meal can sustain a female mosquito for a few days, whereas multiple blood meals will further prolong her lifespan.
However, it’s essential to note that female mosquitoes can transmit diseases during their blood-feeding process, making them a significant health concern.
By understanding the factors that influence the lifespan of adult mosquitoes, we gain valuable insights into their life cycle and behavior.
This knowledge can aid in the development of effective mosquito control strategies, ultimately helping to mitigate the spread of mosquito-borne diseases.
The Aftermath Of Biting: The Fate Of The Mosquito
Have you ever wondered what happens to a mosquito after it bites someone?
The fate of mosquitoes can vary depending on numerous factors such as their lifespan, the impact of disease transmission, and the variations among different mosquito species.
We will delve into these aspects and gain insights into the life and fate of mosquitoes after they have had their blood meal.
What Happens After A Mosquito Bites Someone?
After a mosquito bites someone, it’s not all smooth sailing for the tiny bloodsucker.
Many mosquitoes face a tumultuous journey ahead. Once a mosquito has successfully fed on a warm-blooded host, it enters a critical phase in its life cycle.
The blood that it ingests provides the necessary nutrients for the female mosquito to develop and produce eggs.
This blood meal kickstarts a series of physiological changes within the mosquito’s body.
The mosquito goes through a digestion process, where the proteins and other nutrients from the blood are broken down and utilized for egg development.
Mosquito Lifespan Post-blood Meal: A Decisive Factor
The lifespan of a mosquito post-blood meal plays a crucial role in determining its fate.
Female mosquitoes, which are the ones responsible for biting and transmitting diseases, generally live longer than male mosquitoes.
This extended lifespan allows them to complete their reproductive cycle.
On average, female mosquitoes can live for around 2 to 4 weeks. However, there are variations among different mosquito species.
Some species may have shorter lifespans, while others can live up to 8 weeks or longer.
| Mosquito Species | Average Lifespan (Female) |
|---|---|
| Anopheles | 2-4 weeks |
| Aedes aegypti | 2-4 weeks |
| Culex | 2-4 weeks |
| Aedes albopictus | 4-8 weeks |
As you can see, the lifespan of a mosquito can depend on the species, and this, in turn, affects its ability to transmit diseases.
The Impact Of Disease Transmission On Mosquito Lifespan
When a mosquito bites an infected person or animal, it can become a carrier of various diseases.
The fate of the mosquito changes dramatically when it becomes a vector for diseases such as malaria, dengue, or Zika.
Once a mosquito carries a disease, it can pass it on to other hosts through subsequent bites.
However, the transmission of diseases can also take a toll on the mosquito’s lifespan.
Some studies suggest that the presence of certain pathogens can reduce the mosquito’s lifespan by interfering with its immune system and overall health.
Understanding The Lifespan Variation Among Different Mosquito Species
As mentioned earlier, different mosquito species display variations in their lifespans.
These variations can be attributed to various factors such as habitat, climate, and reproductive behaviors.
Some species, like the Aedes albopictus, are known to have longer lifespans compared to others.
Understanding the lifespan variation among different mosquito species is crucial for developing effective mosquito control strategies.
By targeting specific species with longer lifespans, it becomes possible to reduce the overall mosquito population and consequently minimize disease transmission.
Controlling Mosquito Populations: Implications For Lifespan
Understanding the lifespan of mosquitoes is crucial in devising effective strategies to control their populations.
By targeting factors that influence their longevity, we can implement measures to minimize their lifespans and subsequently reduce the risks they pose.
We explore the role of mosquito control in reducing lifespan, techniques for managing their populations, the impact of environmental factors, and potential longevity strategies.
The Role Of Mosquito Control In Reducing Lifespan
Mosquito control plays a vital role in reducing the lifespan of these tiny but formidable insects.
By implementing measures aimed at interrupting their life cycle, we can effectively hinder their ability to transmit diseases and create a nuisance.
Below are some techniques commonly used for mosquito control:
Techniques For Mosquito Control And Lifespan Management
- Source Reduction: Eliminating or reducing mosquito breeding sites is a fundamental approach to control their populations. This can be achieved by regularly removing stagnant water from containers, clearing gutters, and properly maintaining outdoor areas.
- Mosquito Larvicides: Applying larvicides to standing water that cannot be eliminated can help control mosquito larvae. Larvicides target the developmental stages of mosquitoes, disrupting their growth and preventing them from becoming adult mosquitoes.
- Mosquito Traps: Utilizing mosquito traps can effectively reduce the number of adult mosquitoes in an area. These traps attract and capture mosquitoes, helping to decrease their population and overall lifespan.
- Insecticides: Spraying insecticides can be an effective method to control adult mosquitoes. However, it’s important to use environmentally friendly and targeted insecticides to minimize the impact on non-target organisms.
The Impact Of Environmental Factors On Mosquito Lifespan
Environmental factors greatly influence the lifespan of mosquitoes. Temperature, humidity, and availability of suitable habitats are key factors determining their survival and ability to reproduce.
Mosquitoes thrive in warm and humid environments, which support their development and increase their lifespan.
Conversely, unfavorable conditions such as extreme cold or dryness can significantly reduce their populations.
Additionally, the availability of blood meals, which is necessary for female mosquitoes to lay eggs, impacts their lifespan.
Mosquitoes that have a readily available source of blood can live longer and produce more offspring compared to those with limited access.
Longevity Strategies For Mosquitoes: Seeking Effective Solutions
As researchers continue to study mosquitoes and their behaviors, several current and potential longevity strategies are being explored.
These include:
- Genetic Modification: Scientists are investigating the feasibility of genetically modifying mosquitoes to render them incapable of transmitting diseases or to disrupt their reproduction cycles, thereby reducing their lifespan.
- Biological Control: Introducing mosquito predators such as fish and certain insects into mosquito breeding areas can help control their populations and ultimately reduce their lifespan.
- Public Awareness and Education: Raising awareness about mosquito-borne diseases and promoting preventive measures, such as using insect repellents and wearing protective clothing, can contribute to reducing the lifespan of mosquitoes by minimizing human exposure to potential blood meals.
FAQs For How Long Does A Mosquito Live After Biting Someone
How Long Does A Mosquito Live After Biting Someone?
A mosquito typically lives for about one to two months after biting someone.
How Long Can A Mosquito Survive Without Food?
A mosquito can survive for up to two weeks without feeding on blood or obtaining nutrients.
Can A Mosquito Bite More Than One Person?
Yes, mosquitoes can bite multiple people in a single feeding session, seeking a blood meal for each.
What Happens To A Mosquito After It Bites Someone?
After biting someone, female mosquitoes use the blood to nourish their eggs, while males do not require blood and primarily feed on nectar.
Final Words
The lifespan of a mosquito typically ranges from a few weeks to a few months, depending on various factors.
After biting someone, a female mosquito can live for another few days to a week, while a male mosquito has a shorter lifespan.
Understanding the lifespan of mosquitoes can help in controlling their population and preventing the spread of diseases they carry.
By taking necessary precautions and adopting effective mosquito control methods, we can minimize their impact on our lives and health. Stay informed, stay protected!
